Cusabio N-terminal 6xHis-Avi-tagged Recombinant
Description
Recombinant human CD55 spanning amino acids 35-353. This construct contains a C-terminal Avi-Tag followed by a C-terminal His tag (6xHis). The recombinant protein was enzymatically biotinylated using N-terminal 6xHis-Avi-tagged Recombinant and affinity purified.
Construct: CD55 (35-353-Avi-His)-(biotin)
Species: Human
Host species: HEK293
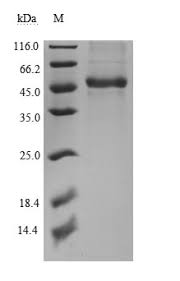
MW: 38kDa
Glycosylation: This protein runs at a higher MW by SDS-PAGE due to glycosylation.
Genbank: #NM_000574
Tag(s): C-terminal Avi-His-Tag
Label: This protein is enzymatically biotinylated using Avi-Tag™ technology. Biotinylation is confirmed to be ≥90%.
Amino acids: 35-353
UniProt: #P08174
Storage stability: At least 6 months at -80°C.
Synonym(s): Molecule CD55, CR, CROM, Cromer blood group, DAFF, 100943-1, 100943-2
Purity: ≥90%
Formulation: 8 mM phosphate pH 7.4, 110 mM NaCl, 2.2 mM KCl, 20% glycerol.
Warnings: Avoid freeze/thaw cycles.
Scientific Category: Immunotherapy
Regulatory Status: For Research Use Only

Technology
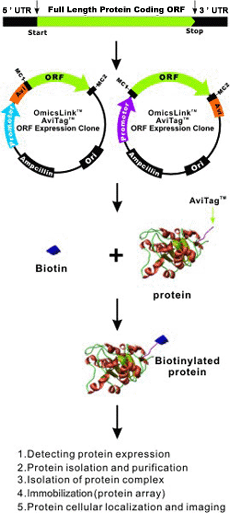
AviTag™ technology is based on the biotinylation of AviTag™ by biotin ligase in vitro or in vivo and the specific and reversible binding of avidin or streptavidin to biotin to immobilize, purify and visualize proteins.
Combined with OmicsLink™ expression-ready clones
GeneCopoeia offers AviTag™ technology in a wide range of expression vectors. For example, it has been combined with the IRES (internal ribosome entry site) element and SUMO, 6xHIS, and a variety of other tags. The AviTag with promoters driven by T7 or CMV is available for more than 20,000 human and 15,000 mouse genes.
Specific
The biotinylation of the recombinant protein carried by the AviTag is highly specific. In the presence of biotin and ATP, biotin ligase catalyzes the amide bond between biotin and the peptide-specific lysine 15-aa AviTag. Biotinylated proteins in nature are extremely rare, which makes the chances of cross-reactions, especially compared to antibodies, very low.
Advantages over chemical labelling of biotin
- During chemical labelling with biotin, the protein can be inactivated due to random biotinylation of the protein surface by binding of biotin to the catalytic or binding domains of the protein. With Avi-Tag, virtually any protein can be easily and efficiently biotinylated in vivo or in vitro using the unique AviTag site.
- Avi-Tag biotinylation is performed enzymatically, resulting in mild reaction conditions and highly specific tagging.
- Biotin-AviTag is 15 amino acids long, which is one-fifth of most alternative biotinylation tag sequences that are greater than 85 amino acid residues long; an important consideration if steric conflicts are to be minimized.